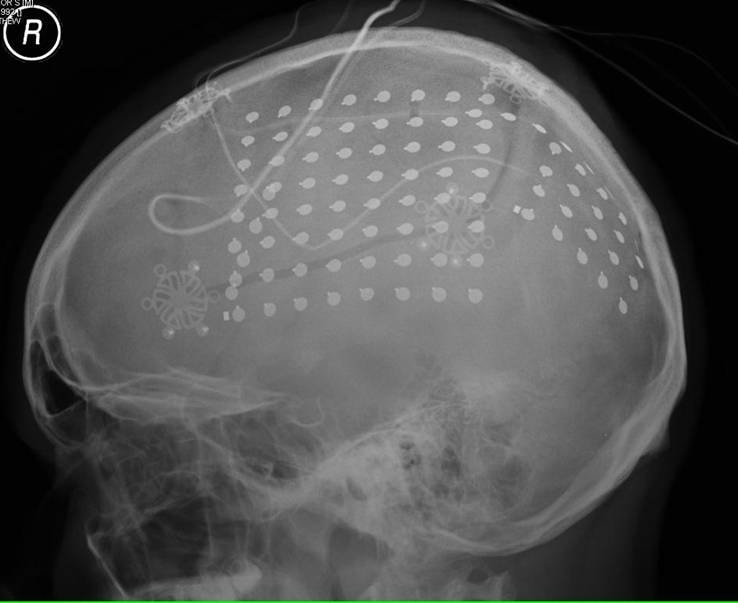
Evaluation of epilepsy patients for whom surgery is contemplated sometimes requires simultaneous MRI (for anatomic localization) with (functional) electroencephalography (EEG) recording. The EEG signal may be obtained from superficial scalp electrodes and/or from surgically implanted depth electrodes or subdural strips/grids.
The primary MR safety concern is RF-induced heating at the electrode tips or contact points. This risk can be minimized by using specifically designed MR-compatible electrodes, transmit-receive head coils, low SAR sequences, separating the wires, and directing them posteriorly out of the scanner.
For scalp recording during MRI, several companies (e.g., Natus, Rhythmlink, PMT) offer MR Conditional cup electrodes made of Ag/AgCl-coated plastic with nichrome (Ni-Cr) wires. Just a single company (Ad-Tech) produces MR Conditional depth and surface electrodes. They are made of platinum-iridium (Pt-Ir) and produce only a minor artifact on MRI.
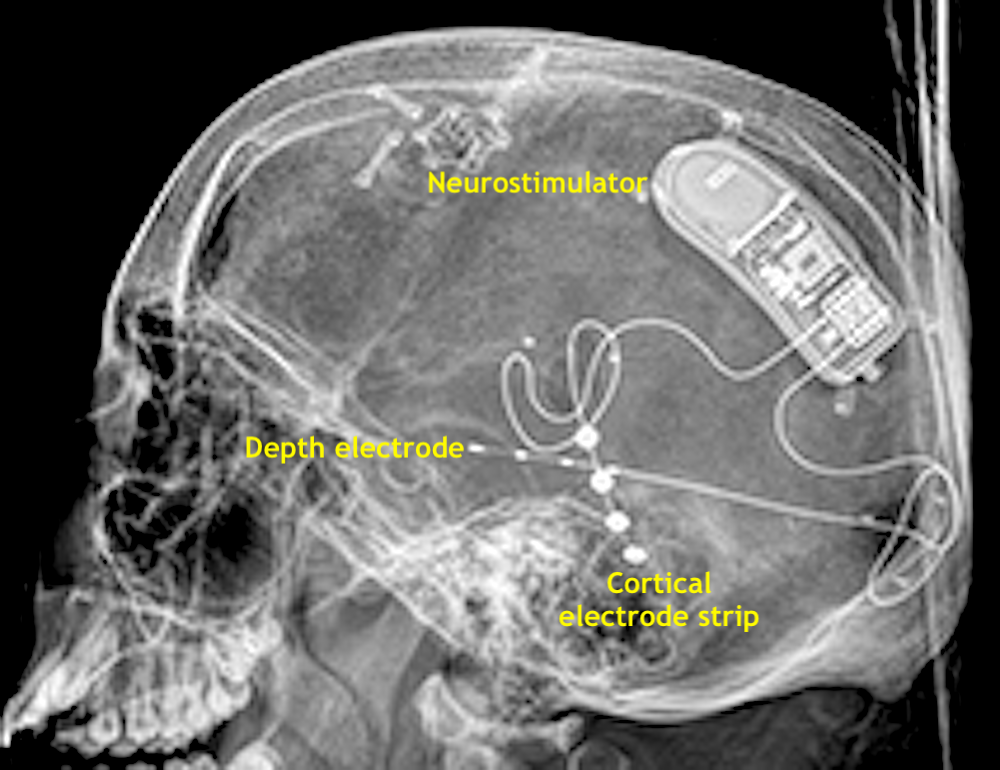
Both depth and cortical electrodes are present in the NeuroPace® RNS system. This device, sometimes referred to as a "brain pacemaker", senses abnormal EEG foci and provides personally tailored stimuli to disrupt seizure activity. It is considered MR Unsafe.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Carmichael DW, Thornton JS, Rodionov R, et al. Safety of localizing epilepsy monitoring intracranial electroencephalograph electrodes using MRI: radio frequency-induced heating. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 28:1233-1244. [DOI LINK]
Ciumas C, Schaefers G, Bouvard S et al. A phantom and animal study of temperature changes during fMRI with intracerebral depth electrodes. Epilepsy Res 2013; 108:57–65. [DOI LINK]
Hawsawi HB, Carmichael DW, Lemieux L. Safety of simultaneous scalp or intracranial EEG during MRI: a review. Front Phys 2017; 5:42. [DOI LINK]
Peedicail JS, Poulin T, Scott JN, et al. Clinical safety of intracranial EEG electrodes in MRI at 1.5 T and 3 T: a single-center experience and literature review. Neuroradiology 2021 (on-line) [DOI LINK]
Shah AK, Mittal S. Invasive electroencephalography monitoring: Indications and presurgical planning. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 2014;17, Suppl S1:89-94
Carmichael DW, Thornton JS, Rodionov R, et al. Safety of localizing epilepsy monitoring intracranial electroencephalograph electrodes using MRI: radio frequency-induced heating. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 28:1233-1244. [DOI LINK]
Ciumas C, Schaefers G, Bouvard S et al. A phantom and animal study of temperature changes during fMRI with intracerebral depth electrodes. Epilepsy Res 2013; 108:57–65. [DOI LINK]
Hawsawi HB, Carmichael DW, Lemieux L. Safety of simultaneous scalp or intracranial EEG during MRI: a review. Front Phys 2017; 5:42. [DOI LINK]
Peedicail JS, Poulin T, Scott JN, et al. Clinical safety of intracranial EEG electrodes in MRI at 1.5 T and 3 T: a single-center experience and literature review. Neuroradiology 2021 (on-line) [DOI LINK]
Shah AK, Mittal S. Invasive electroencephalography monitoring: Indications and presurgical planning. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 2014;17, Suppl S1:89-94
Related Questions
Can patients with deep brain stimulators be scanned?
How do you deal with peripheral nervous system stimulators from an MR safety perspective?
Can patients with deep brain stimulators be scanned?
How do you deal with peripheral nervous system stimulators from an MR safety perspective?