|
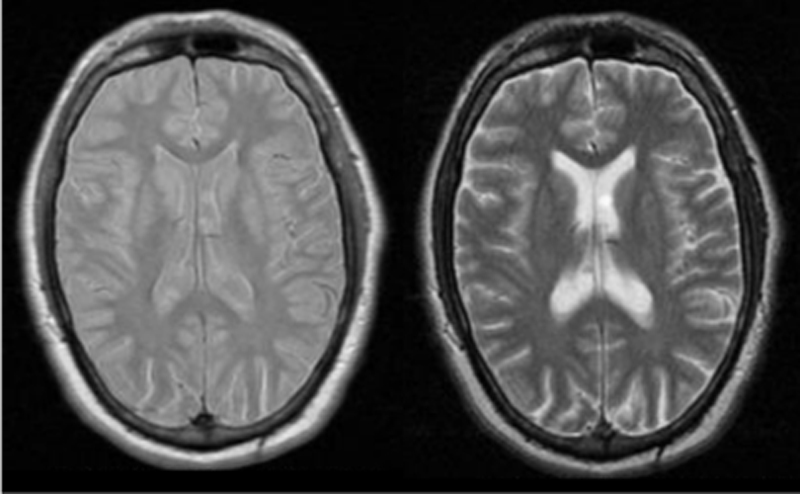
For the first 20 years of clinical MRI, double-echo sequences were part of standard protocols for nearly all body parts. Short and long echo times (TE) were used to generate proton-density and T2-weighted images in a single acquisition using a long repetition time (TR). Over the last decade T2-FLAIR has largely replaced proton-density sequences for neuroimaging, but they are still used in musculoskeletal and other body applications.
|
Dual-echo FSE images can be obtained through a process known as view sharing. Zero and low-amplitude phase encoding steps are performed both early and late along the FSE echo train. This produces two sets of low spatial frequency images with short and long effective TE's (typically TE1eff at <20 ms and TE2eff at >80 ms) reflecting the dominant image contrast of spin-density and T2-weighting. Signals from remaining intermediate and high-amplitude phase encoding steps that contain edge details are shared between the two data sets for final image reconstruction.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Johnson B, Fram EK, Drayer BP, et al. Evaluation of shared-view acquisition using repeated echoes (SHARE): a dual-echo fast spin-echo MR technique. Am J Neuoradiol 1994;15:667-673.
Mekle R, Laine AF, Wu EX. Combined MR data acquisition of mulitcontrast images using variable acquisition parameters and k-space data sharing. IEEE Transact Med Imaging 2003; 22:806-823.
Johnson B, Fram EK, Drayer BP, et al. Evaluation of shared-view acquisition using repeated echoes (SHARE): a dual-echo fast spin-echo MR technique. Am J Neuoradiol 1994;15:667-673.
Mekle R, Laine AF, Wu EX. Combined MR data acquisition of mulitcontrast images using variable acquisition parameters and k-space data sharing. IEEE Transact Med Imaging 2003; 22:806-823.
Related Questions
What is Fast (Turbo) spin echo imaging?
What is Fast (Turbo) spin echo imaging?