|
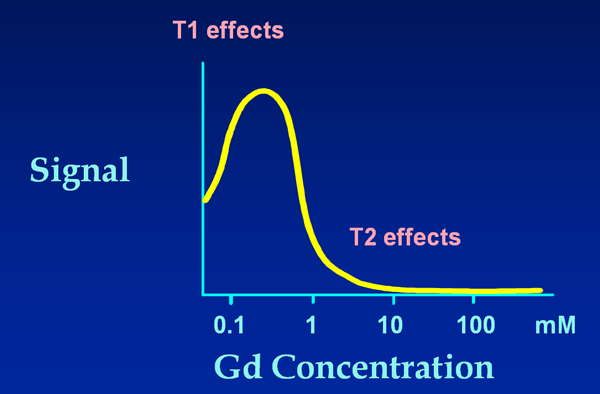
In routine MR imaging, the mild T2-shortening effects of low doses of gadolinium (which decrease signal intensity) are usually overwhelmed by the more dominant T1-shortening effects (which increase signal intensity) and are therefore not normally observed. However, as the concentration of Gd increases, signal intensity will eventually begin to fall. The Gd concentration beyond which signal falls depends on the particular tissue and pulse sequence parameters selected.
|
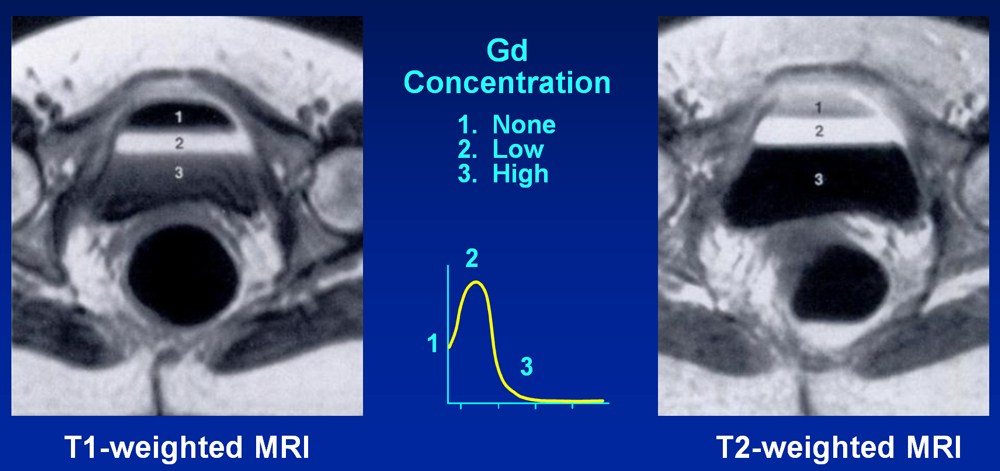
Paradoxically decreased signal intensity of some tumors postcontrast has been reported, but this is a rare phenomenon and is not normally encountered on routine MR images of most tissues using standard doses of gadolinium. In the kidneys and bladder, however, where Gd is excreted and concentrated, tissue and urine levels of Gd may approach 40 mM. At concentrations this high, T2 shortening may result in a significant decrease in signal intensity noticeable on both T1- and T2-weighted images. Urine in the bladder may exhibit an unusual triple-layering phenomenon. T2-shortening effects predominate and a low signal occurs in the bottom pseudolayer where Gd concentration is highest. In the middle layer, moderate concentrations of Gd result in T1 shortening and high MR signal.
Low-T2 signal may occasionally be seen in MR arthrograms and venograms (where high concentrations of gadolinium are injected directly into joints or vessels); and in the "first pass" of gadolinium contrast through the vascular system on dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) studies or time-resolved MR angiography. The later is more properly considered a T2* (susceptibility) effect that will be described in later Q&As.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Elster AD, Sobol WT, Hinson WH. Pseudolayering of Gd-DTPA in the urinary bladder. Radiology 1990; 174:379-381.
Rohrer M, Bauer H, Mintorovitch J et al. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions a different magnetic field strengths. Invest Radiol 2005; 40:715-724.
Elster AD, Sobol WT, Hinson WH. Pseudolayering of Gd-DTPA in the urinary bladder. Radiology 1990; 174:379-381.
Rohrer M, Bauer H, Mintorovitch J et al. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions a different magnetic field strengths. Invest Radiol 2005; 40:715-724.
Related Questions
Why does gadolinium apparently only shorten T1? Doesn't it have an effect on T2 as well?
Why does gadolinium apparently only shorten T1? Doesn't it have an effect on T2 as well?