|
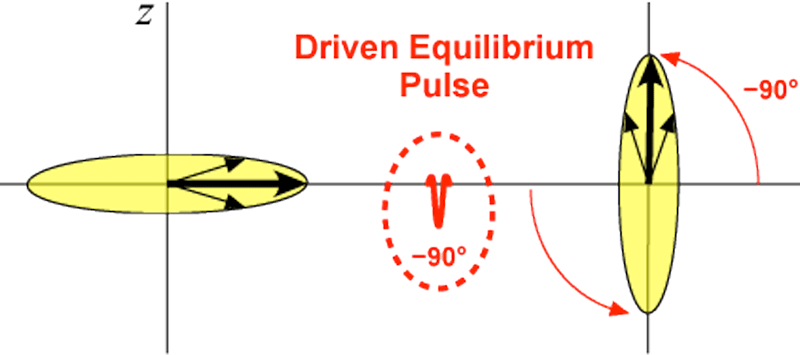
Driven equilibrium (DE), also known as fast recovery, is technique in which a −90º "flip-back" pulse is used to help restore longitudinal magnetization at the end of an MR sequence. In rapid imaging, substances with long T1 and T2 values (like CSF, urine, or bile) may still not have fully recovered their longitudinal magnetization (Mz) by the end of each TR interval. After a number of cycles, saturation occurs and the normal high T2 signals of such fluids are diminished. Driven equilibrium techniques are particularly useful at restoring these signals and are widely employed in spinal imaging, MR urography, and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP).
|
Driven equilibrium pulses may be used in conjunction with virtually any imaging or spectroscopy sequence, but are most commonly employed with Fast/Turbo spin echo imaging. All major MR vendors offer these sequences under different trade names: Siemens' RESTORE, GE's Fast recovery fast spin echo (FRFSE), Philips' DRIVE, Hitachi's Driven equilibrium FSE, and Cannon's T2 Plus FSE. Occasionally the generic acronym DEFT (Driven Equilibrium Fourier Transform) is used. A typical 2D fast spin echo implementation is shown below.
A cluster of three nonselective pulses in DE pattern (+90º/180º/−90º) may be used as a preparatory module for spectroscopy, echo-planar imaging, and GRE sequences like MP-RAGE. Because T2-decay occurs during the time between these pulses, the module imparts T2 sensitivity and is thus often called a T2-prep pulse.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Because flip angles of the DE pulses may differ slightly from ideal values, crusher gradients surrounding the 180º-pulse and a spoiler gradient after the flip-back 90º-pulse are used to interference from residual transverse magnetization.
References
Becker ED, Ferretti JA, Farrar TC. Driven equilibrium Fourier transform spectroscopy. A new method of nuclear magnetic resonance signal enhancement. J Am Chem Soc 1969;91:7784-5. (This was the first use of a DE pulse — to improve the signal in NMR spectroscopy)
Melhem ER, Itoh R, Folkers PJM. Cervical spine: three-dimensional fast spin-echo MR imaging − improved recovery of longitudinal magnetization with driven equilibrium pulse. Radiology 2001; 218:283-288. (Good description of how DE pulses can be used to augment CSF signal in 3D FSE imaging).
van Uijen CM, den Boef JH. Driven-equilibrium radiofrequency pulses in NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 1984;1:502-7. (One of the earliest implementation of DE pulses for imaging).
Becker ED, Ferretti JA, Farrar TC. Driven equilibrium Fourier transform spectroscopy. A new method of nuclear magnetic resonance signal enhancement. J Am Chem Soc 1969;91:7784-5. (This was the first use of a DE pulse — to improve the signal in NMR spectroscopy)
Melhem ER, Itoh R, Folkers PJM. Cervical spine: three-dimensional fast spin-echo MR imaging − improved recovery of longitudinal magnetization with driven equilibrium pulse. Radiology 2001; 218:283-288. (Good description of how DE pulses can be used to augment CSF signal in 3D FSE imaging).
van Uijen CM, den Boef JH. Driven-equilibrium radiofrequency pulses in NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 1984;1:502-7. (One of the earliest implementation of DE pulses for imaging).
Related Questions
What is Fast (Turbo) Spin Echo imaging?
What is Fast (Turbo) Spin Echo imaging?