|
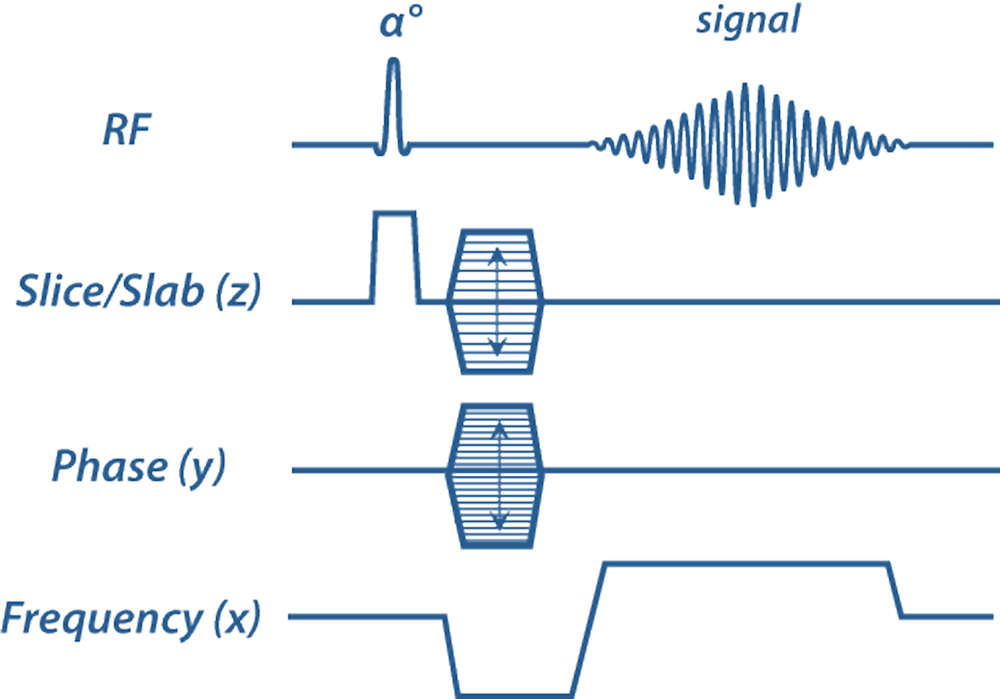
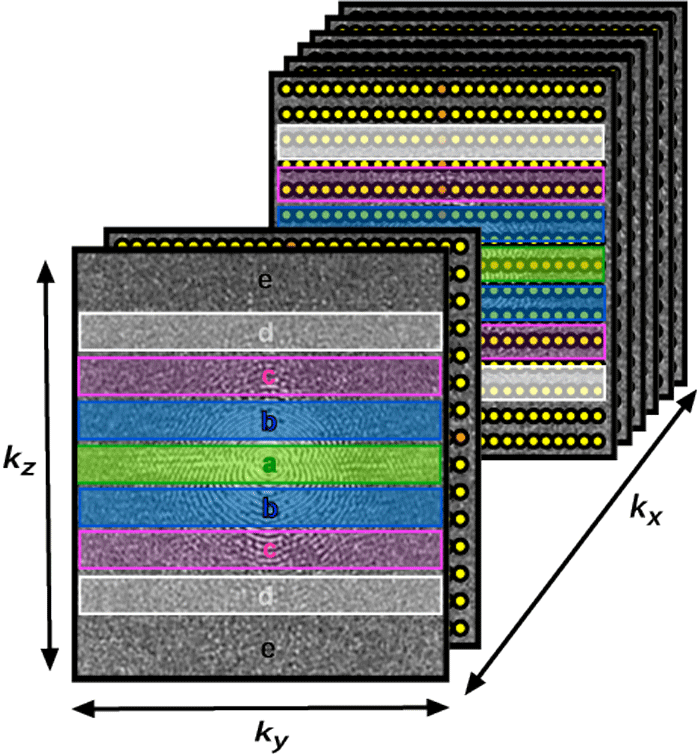
Contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA) is typically performed in three-dimensional (3D) mode, generating a rectangular (Cartesian) array of data. This scheme uses a single frequency-encoding direction (x) and two phase-encoding directions (y,z). To reduce imaging time fewer phase-encoding steps are often acquired in the slice/slab direction (z), giving rise to slightly anisotropic voxels and an asymmetric 3D k-space matrix.
|
|
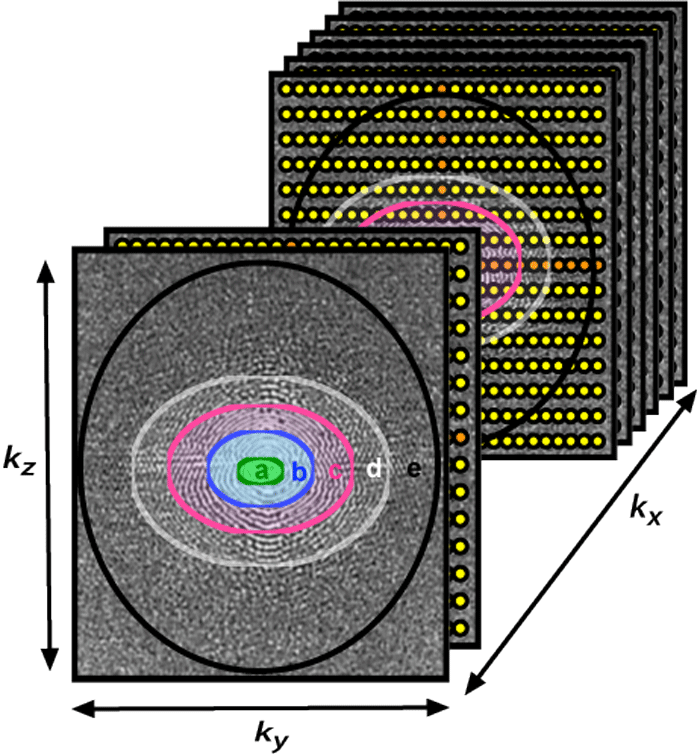
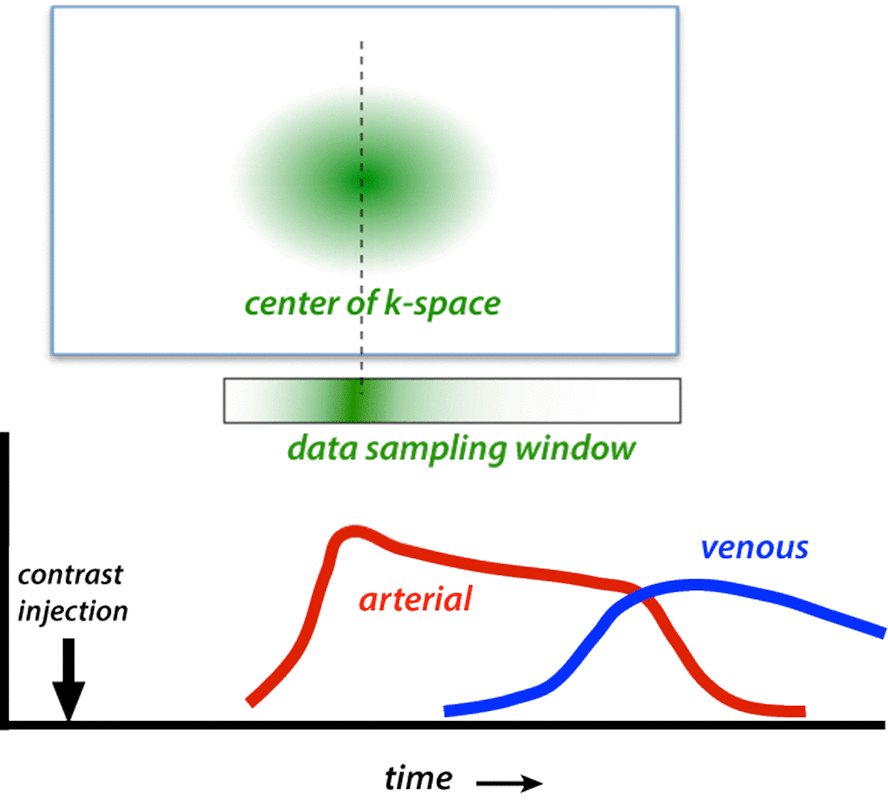
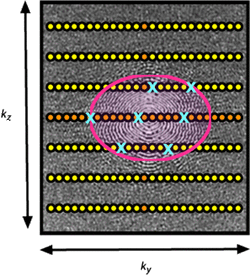
In all forms of centric ordering the lowest spatial frequency points (near the center of k-space) are sampled first. These central points contribute most to overall image contrast, which is timed to correspond to the arrival of the arterial bolus. In addition to accentuating arterial signal, centric order also minimizes venous signal because appearance of contrast in the venous system occurs during the time when high spatial frequencies (edges/details) are being sampled. Some vendors allow the center of k-space data collection to be moved asymmetrically within the data sampling window. This variation has been called recessed elliptical centric ordering.
|
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
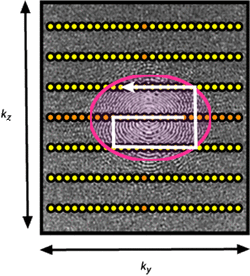
One modification of all centric methods concerns the actual order data points are acquired within a given layer or ellipse. Most manufacturers use a structured method of data sampling beginning at the center of k-space, proceeding outward in a spiral or zig-zag direction. Here it is desirable to have the middle point of k-space) coincide with the peak arterial bolus. However, some theoretical benefits exist for randomizing data collection within the center of k-space. By sampling the central region of k-space in a random (stochastic) fashion over the full arterial window, the first view does not have to coincide exactly with the bolus peak. This may reduce artifacts occurring from slight mistiming of maximum bolus arrival. Philips' CENTRA and Siemens' TWIST methods utilize this randomized sampling technique.
McNeal GR, Natsuaki Y, Kroeker R, et al. Improved workflow and performance for contrast-enhanced MR angiography sequences. MAGNETOM Flash 2009;2:95-98. (Sales brochure including discussion of Siemens time-to-peak view ordering adjustment)
Watts R, Wang Y, Prince MR. Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography. US Patent # 7,003,343 B2, filed Feb 21, 2006.
Willinek WA, Gieseke J, Conrad R, et al. Randomly segmented central k-space ordering in high-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the supraaortic arteries: initial experience. Radiology 2002; 225:583-588. (Description of Philips CENTRA method).
Wilman AH, Riederer SJ, King BF, et al. Fluoroscopically triggered contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography with elliptical centric view order: application to the renal arteries. Radiology 1997; 205:137-146.
How do you compute the arrival of contrast in a vessel to know when to start the MR acquisition?