Like spinal cord stimulation, the primary indication for peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) is localized or regional pain refractory to conventional therapies. A variety of purely external transcutaneous stimulation devices (Aleve® Direct Therapy and other TENS units; H-WAVE®, ActiPatch® ) or percutaneous neuromodulation devices that are predominantly external but have wires or needles passing through the skin (PNT®, Deepwave®, SPRINT®) will not be discussed further here. These are all MR Unsafe and must be removed prior to MRI. Instead this Q&A will focus on peripheral neurostimulators with electrodes that are completely implanted.
The earliest implanted peripheral neurostimulators utilized similar technology to then existing spinal cord stimulators and were MR Unsafe. Examples include the Renew®, Genesis®, and Eon® Systems (Abbott/St. Jude) and the Legacy L300™ foot drop system (Bioness). Most, but not all, modern PNS systems do not contain implanted pulse generators and are MR Conditional.
|
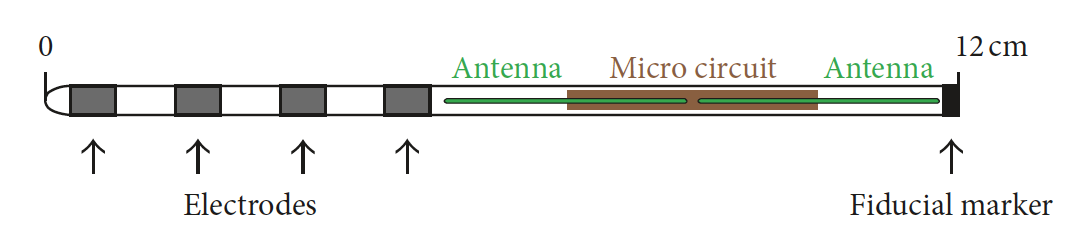
The StimWave StimQ® (StimWave Technologies) exemplifies this new generation of PNS devices. The implanted lead is only 1 mm in diameter and can be percutaneously inserted through a needle. It contains an antenna, microcircuitry, and 4-9 terminal electrodes placed near the target nerve. An external transmitter placed over the skin near the the antenna portion delivers electrical pulses to the nerve. The StimQ® is MR Conditional at 1.5T, but earlier models (like the Freedom 8A) are MR Unsafe.
|
The StimRouter® PNS system (Bioness) is similar to the StimQ® in that it consists of a single implanted lead with a stimulation end (placed near the nerve) and a receiver end (placed subcutaneously). A matchbox-sized, battery-operated external pulse transmitter stimulates the lead and subsequently the nerve. The StimRouter is MR Conditional at 1.5T and 3.0T (with the external transmitter removed). The entire device should lie outside the physical limits of the RF transmit coil used (body, head, knee, etc.)
 MR Conditional Nalu PNS
MR Conditional Nalu PNS
The Nalu System (Nalumed) consists of an implanted miniature stimulator whose hairbrush leads are set in close proximity to the target peripheral nerve. The stimulator is inductively powered by a battery-containing “therapy disc,” which is worn on the skin directly over the implant. The Nalu is MR Conditional (with the external components removed). Special conditions include performing impedance checks before and after scanning, and using exclusively transmit/receive head or extremity coils for imaging.

Initially met with skepticism, electrical stimulation of the posterior tibial nerve is now a scientifically proven treatment for overactive bladder. The exact mechanism is unknown, but peripheral electrostimulation apparently disrupts neural pathways of the lower urinary tract and modulates higher spinal or brainstem reflexes for micturition.
There is only one implantable tibial nerve stimulator system now manufactured, BlueWind RENOVA™ (MR Conditional at 1.5T and 3.0T). Another legacy tibial nerve stimulator, the Urgent-SQ, may occasionally be encountered. Both devices include a passive receiver element with electrodes implanted near the tibial nerve and require an additional external pulse generator that sends power and stimuli to the receiver transcutaneously.
There is only one implantable tibial nerve stimulator system now manufactured, BlueWind RENOVA™ (MR Conditional at 1.5T and 3.0T). Another legacy tibial nerve stimulator, the Urgent-SQ, may occasionally be encountered. Both devices include a passive receiver element with electrodes implanted near the tibial nerve and require an additional external pulse generator that sends power and stimuli to the receiver transcutaneously.
 MR Conditional Pulsante™ SPG stimulator (modified from Fontaine under CC BY)
MR Conditional Pulsante™ SPG stimulator (modified from Fontaine under CC BY)
The Pulsante™ Microstimulator (Unity HA), previously known as the ATI Neurostimulator, is used to treat debilitating headaches by stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) at the skull base. The receiver portion of the device consists of a lead with 6 stimulating electrodes and a malleable plate for screw fixation to the maxilla. An external transmitter/controller is placed over the face to deliver tailored electrical pulses on demand for headache.
The Pulsante™ is considered MR Conditional up to 3.0T. The external controller, of course, is MR Unsafe cannot be brought into the scanner room.
The Pulsante™ is considered MR Conditional up to 3.0T. The external controller, of course, is MR Unsafe cannot be brought into the scanner room.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Billet B, Wynendaele R, Vanquathem NE. Wireless neuromodulation for chronic back pain: delivery of high-frequency dorsal root ganglion stimulation by a minimally invasive technique. Hindawi Case Reports in Medicine 2017; Article ID 4203271, 4 pages [DOI LINK]
Fontaine D, Santucci S, Lanteri-Minet M. Managing cluster headache with sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation: a review. J Pain Res 2018; 11:375-381.
Nwazota N, Pyati S, Fisher k, Roy L. Device review: Pulsante™ sphenopalatine ganglion microstimulator. Pain Manag 2019; 9:535–541. [DOI LINK]doi.org/10.2217/pmt-2018-0082
StimRouter® Neuromodulation System Clinician’s Guide. Bioness, Inc. 2020. (As always, consult the manufacturer’s web site for the most updated version).
Sweet JA, Mitchell LS, Narouze S, et al. Occipital nerve stimulation for the treatment of patients with medically refractory occipital neuralgia: Congress of Neurological Surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guideline. Neurosurgery 2015; 77 (3): 332-341. [DOI LINK]
Billet B, Wynendaele R, Vanquathem NE. Wireless neuromodulation for chronic back pain: delivery of high-frequency dorsal root ganglion stimulation by a minimally invasive technique. Hindawi Case Reports in Medicine 2017; Article ID 4203271, 4 pages [DOI LINK]
Fontaine D, Santucci S, Lanteri-Minet M. Managing cluster headache with sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation: a review. J Pain Res 2018; 11:375-381.
Nwazota N, Pyati S, Fisher k, Roy L. Device review: Pulsante™ sphenopalatine ganglion microstimulator. Pain Manag 2019; 9:535–541. [DOI LINK]doi.org/10.2217/pmt-2018-0082
StimRouter® Neuromodulation System Clinician’s Guide. Bioness, Inc. 2020. (As always, consult the manufacturer’s web site for the most updated version).
Sweet JA, Mitchell LS, Narouze S, et al. Occipital nerve stimulation for the treatment of patients with medically refractory occipital neuralgia: Congress of Neurological Surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guideline. Neurosurgery 2015; 77 (3): 332-341. [DOI LINK]
Related Questions
What MRI limitations are there for scanning epilepsy patients with superficial or depth electrodes?
What MRI limitations are there for scanning epilepsy patients with superficial or depth electrodes?