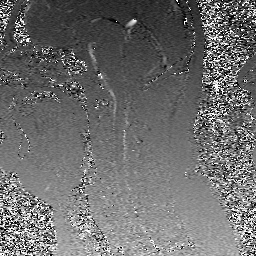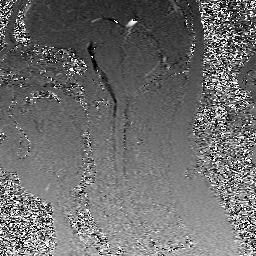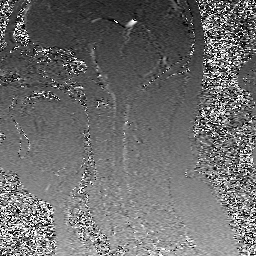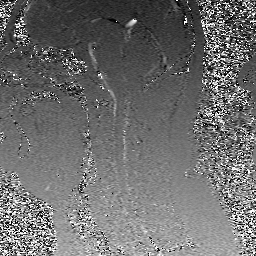
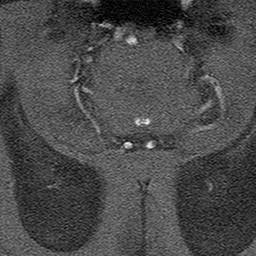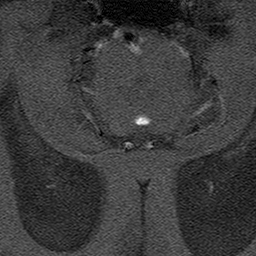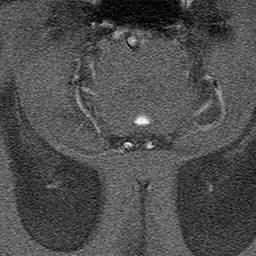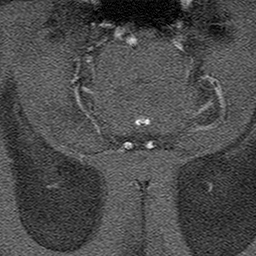
Because phase shift is proportional to velocity, phase-contrast MR methods can be used to quantify moving fluids such as blood in arteries and veins or cerebrospinal fluid within the skull or spine.
Phase-contrast MR can detect flow in the three cardinal directions along which bipolar encoding gradients are applied. This allows calculation of three velocity vector components: vx, vy, and vz. These components be displayed as separate images using using a gray scale to define direction (superior-to-inferior, left-to-right, or anterior-to-posterior). Alternatively, the velocities may be combined into a single magnitude image, where the intensity of each voxel is proportional to the speed (S) given by
Phase-contrast MR can detect flow in the three cardinal directions along which bipolar encoding gradients are applied. This allows calculation of three velocity vector components: vx, vy, and vz. These components be displayed as separate images using using a gray scale to define direction (superior-to-inferior, left-to-right, or anterior-to-posterior). Alternatively, the velocities may be combined into a single magnitude image, where the intensity of each voxel is proportional to the speed (S) given by
These two displays (velocity-encoded and magnitude images) are illustrated below.
|
Either retrospective or prospective cardiac gating may be employed, enabling the measurement of flows through different phases of the cardiac cycle. A region of interest cursor is placed over a particular vessel, producing a graph of maximum flow velocity calculated at that point as a function of time after the R-wave trigger.
Individual images from the flow study may be displayed or they may be viewed in a cine loop. |
Once the mean velocity (V) is computed across a vessel, the cross-sectional area (A) can be measured and flow (Q) calculated by the formula: Q = V x A.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Bryant DJ, Payne JA, Firmin DN, et al. Measurement of flow with NMR imaging using a gradient pulse and phase difference technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984;8:588-93.
Firmin DN, Nayler GL, Klipstein RH, et al. In vivo validation of MR velocity imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:751-6.
Lotz J, Meier C, Leppert A, Galanski M. Cardiovascular flow measurement with phase-contrast MR imaging: basic facts and implementation. Radiographics 2002; 22:651-671.
Bryant DJ, Payne JA, Firmin DN, et al. Measurement of flow with NMR imaging using a gradient pulse and phase difference technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984;8:588-93.
Firmin DN, Nayler GL, Klipstein RH, et al. In vivo validation of MR velocity imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:751-6.
Lotz J, Meier C, Leppert A, Galanski M. Cardiovascular flow measurement with phase-contrast MR imaging: basic facts and implementation. Radiographics 2002; 22:651-671.
Related Questions
How accurate are MR methods to measure flow? What are the artifacts and pitfalls?
What is the 4th dimension in 4D Flow imaging?
How accurate are MR methods to measure flow? What are the artifacts and pitfalls?
What is the 4th dimension in 4D Flow imaging?