Note: In this Q&A we adopt the convention that substances "bright" on T1-weighed images have short T1 values. This is true for most (but not all) pulse sequences. For a detailed explanation, click here.
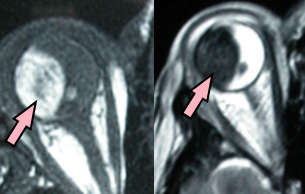
Not only is melanin bright on T1-weighted images, it is also dark on T2-weighted images. It thus has both short T1 and short T2 values.
|
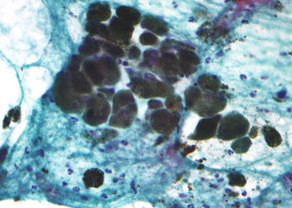
Melanin has a high affinity for metal ions, especially copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. One of melanin's important physiological functions is to serve as a scavenger of free metals and radicals. Approximately one out of every 5 subunits is complexed to a metal ion. The dominant T1 and T2 shortening reflects the paramagnetic effect of these ions.
Melanoma metastases have a propensity to hemorrhage, and so the paramagnetic effects of blood products (especially methemoglobin) may also result in T1 and T2 shortening in these lesions. |
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Enochs WS, Petherick P, Bogdanova A, et al. Paramagnetic metal scavenging by melanin: MR imaging. Radiology 1997;204:417-423
Enochs WS, Petherick P, Bogdanova A, et al. Paramagnetic metal scavenging by melanin: MR imaging. Radiology 1997;204:417-423
Related Questions
What is T1 relaxation?
Can you explain a little more about the dipole-dipole interaction? I still don't quite understand.
What is T1 relaxation?
Can you explain a little more about the dipole-dipole interaction? I still don't quite understand.