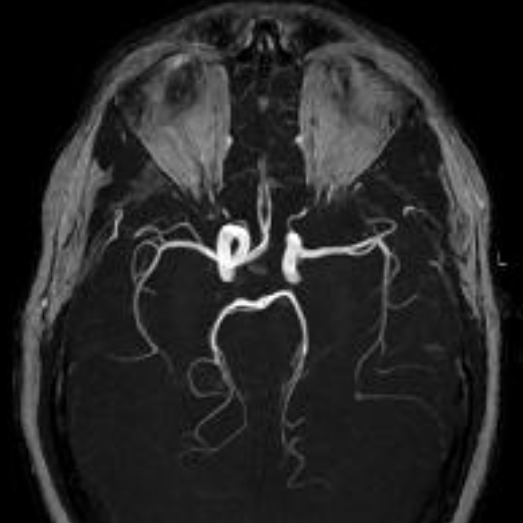
Since time-of-flight MR images are T1-weighted and reformatted using a maximum intensity projection (MIP) method, high signal from fat may obscure vessels or mimic pathology. This is particularly problematic at the skull base where abundant fatty marrow may create artifacts around the carotid and vertebral arteries. As such, a number of centers have explored methods to suppress fat through chemical shift (CHESS), Dixon, or water excitation (WE) techniques. An example using WE is shown below:
Some authorities have reported good success with these methods, expecially for visualizing smaller vessels like the ophthalmic and lenticulostriate arteries. Other sites (including my own) have found these methods create new artifacts that may be worse than those from residual fat signal. Presumably these artifacts (including spurious loss of intravascular signal around curves and bends) are due to imperfect slice profiles with unintended saturation effects.
Keep in mind that fat suppression (or water excitation) methods will not suppress "shine-though" of hematomas, CSF-flow phenomena, motion, or gadolinium — all of which may be much more troublesome than fat. While keeping an open mind toward new developments, I therefore do not recommend these methods be used for routine TOF MRA.
Keep in mind that fat suppression (or water excitation) methods will not suppress "shine-though" of hematomas, CSF-flow phenomena, motion, or gadolinium — all of which may be much more troublesome than fat. While keeping an open mind toward new developments, I therefore do not recommend these methods be used for routine TOF MRA.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
An interesting new TOF saturation technique called BeamSat TOF is available as a product on Hitachi high-field systems. BeamSat TOF allows users to place a cylindrical beam sat pulse over a specific artery while performing a 3D TOF study over a region supplied by several arteries. Signal from that one blood supply will be suppressed, allowing location of sources of blood flow to be identified. For example, a BeamSat Pulse may be placed sequentially over each carotid and vertebral artery to evaluate the contribution of each vessel to portions of the brain or a vascular malformation. For more information, the reader should follow this link to the Hitachi web site.
References
Gizewski ER, Ladd ME, Paul A, et al. Water excitation: a possible pitfall in cerebral time-of-flight angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26:152-155.
Mirowitz SA. Apparent vascular occlusion on cranial TOF MRA with peripheral presaturation technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1993;17:927–931.
Gizewski ER, Ladd ME, Paul A, et al. Water excitation: a possible pitfall in cerebral time-of-flight angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26:152-155.
Mirowitz SA. Apparent vascular occlusion on cranial TOF MRA with peripheral presaturation technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1993;17:927–931.
Related Questions
What are the major TOF MR artifacts should we know about?
What are the major TOF MR artifacts should we know about?