HASTE is an echo-planar fast spin echo sequence trademarked by Siemens. The expanded acronym fairly completely describes what it entails: Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-shot Turbo spin Echo imaging.
Other vendors have similar sequences under slightly different names: GE (Single-shot fast spin echo, SS-FSE), Philips (Single-shot turbo spin echo, SSH-TSE; ultra-fast spin echo, UFSE), HItachi (Single-shot fast SE), and Canon (Fast Advanced Spin Echo, FASE, SuperFASE).
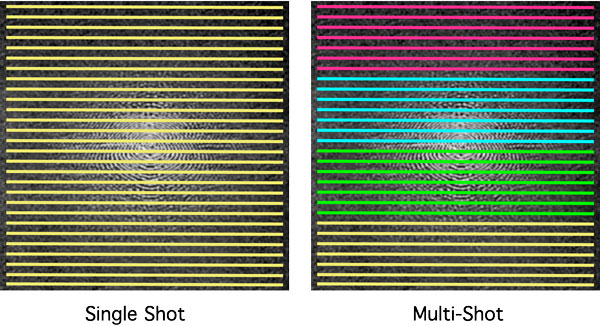
HASTE/SS-FSE is a single-shot technique. This means that data from all of k-space is obtained after a single 90º-excitation pulse. This requires very long echo trains, which in modern scanners may number 128, 256, or even higher.
By comparison, "regular" FSE/TSE is a multi-shot technique. This means that although k-space is traversed much more quickly than in conventional SE imaging, data from several separate RF-excitations are still needed to acquire all the data. For example, if 128 lines of k-space were to be sampled, a FSE/TSE sequence with an ETL/Turbo factor of 16 would require 128/16 = 8 "shots" to completely collect all the data.
To minimize the number of lines sampled, HASTE/SS-FSE uses phase-conjugate symmetry (a partial Fourier method) that takes advantage of certain "mirror-image" properties of k-space and the MR signal. This allows only a little more than half of k-space data to be directly collected, while the remaining lines can be estimated. A typical pulse sequence timing diagram for HASTE/SS-FSE is shown below:
HASTE/SS-FSE techniques have already found robust applications throughout the body, including: routine scout images; images of the head or body in children or uncooperative patients; fetal imaging; non-breath-hold abdominal imaging: MR cholangiopancreatography; MR myelography, and non-contrast MR angiography. By necessity, echo times are relatively long, so HASTE images are typically T2-weighted. However, in conjunction with preparatory inversion pulses they can be made to assume some degree of T1- and spin-density-weighted contrast. A few representative examples are shown below.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Patel MR. Klufas RA, Alberico RA, Edelman RR. Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with fast spin-echo MR in diseases of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997; 18:1635-1640.
Semelka RC, Kelekis NL, Thomasson D, Brown MA, Laub GA. HASTE MR imaging: description of technique and preliminary results in the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging 1996; 6:698-699.
Patel MR. Klufas RA, Alberico RA, Edelman RR. Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with fast spin-echo MR in diseases of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997; 18:1635-1640.
Semelka RC, Kelekis NL, Thomasson D, Brown MA, Laub GA. HASTE MR imaging: description of technique and preliminary results in the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging 1996; 6:698-699.
Related Questions
How does phase-conjugate symmetry work? Why is it used?
How does phase-conjugate symmetry work? Why is it used?