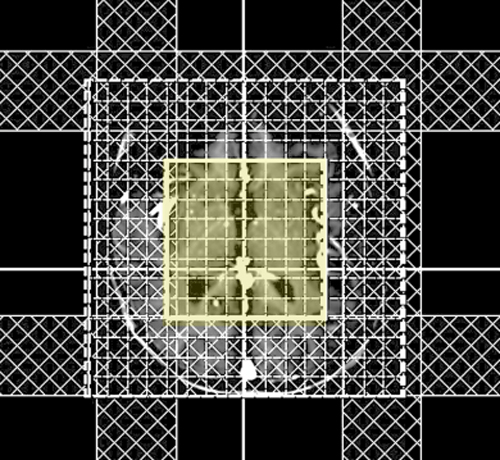
- Obtain whole-head multi-planar scout images. These will be used to set the boundaries of the spectroscopy volume and for placement of saturation bands.
- Pick type of MRS coverage. The first decision is to choose between Single Voxel Spectroscopy (SVS) and Multi-Voxel Chemical Shift Imaging (CSI). If MVSI is chosen then either a 2D method (imaging an array of voxels in a single plane) or 3D method (imaging an entire volume of voxels) must then be selected. In general, SVS methods are easier and quicker to perform with higher signal-to-noise than MVSI, but suffer from poorer spatial resolution.
- Select MRS technique and parameters. Although several MRS sequences are available, some variant of PRESS (Point REsolved SpectoScopy). is most commonly used. Other options include STEAM (Stimulated Echo Acquisition Mode) or simple spin-echo acquisition. Imaging parameters such as TR, TE, FOV, NEX, and voxel size(s) must also be specified. Typically a medium length TR is chosen (1500-2000 msec). Separately acquired short TE (~30 msec) and medium TE (~144 msec) studies are both usually performed to reveal various metabolites to best advantage.
- Place MRS volume over anatomy of interest. Care must be taken that the imaging region does not include fat-containing scalp or bone marrow that may contaminate the spectrum. Outer volume saturation bands are generally required to be placed over these areas to suppress signal from fat.
- Shimming and Calibration. Shimming is fine-tuning of the magnetic field homogeneity by adjusting currents passing though specialized shim coils next to the gradients. Automated shimming is usually sufficient for routine head MRS studies, but manual adjustments may be necessary.
- Perform MRS Imaging. Typical image acquisition times are 5-15 minutes, depending on technique and size of volume studied.
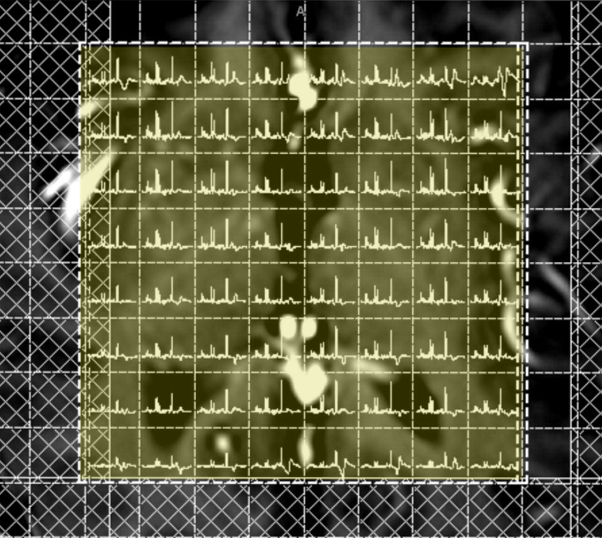
- View/analyze spectra. Separate spectra are generated for each MRS voxel which can then be analyzed visually or overlaid as color maps on anatomic images. Optional post-processing may be performed to identify and quantify detected peaks.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
ACR-ASNR practice guideline for the performance and interpretation of magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the central nervous system. American College of Radiology, Revised 2008.
Bertoldo D, Watcharakorn A, Castillo M. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Introduction and overview. Neuroimag Clin N Am 2013; 23:359-380.
Hajek M, Dezortova M. Introduction to clinical in vivo MR spectroscopy. Eur J Radiol 2008; 67:185-193.
Maudsley AA, Andronesi OC, Barker PB, et al. Advanced magnetic resonance spectroscopic neuroimaging: experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed 2020: e4309.
Posse S, Otazo R, Dager SR, Alger J. MR spectroscopic imaging: principles and recent advances. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013; 37:1301-1325.
Skoch A, Jiru F, Bunke J. Spectroscopic imaging: basic principles. Eur J Radiol 2008; 67:230-239.
Zhu H, Barker PB. MR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging of the brain. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 711:203-226.
ACR-ASNR practice guideline for the performance and interpretation of magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the central nervous system. American College of Radiology, Revised 2008.
Bertoldo D, Watcharakorn A, Castillo M. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Introduction and overview. Neuroimag Clin N Am 2013; 23:359-380.
Hajek M, Dezortova M. Introduction to clinical in vivo MR spectroscopy. Eur J Radiol 2008; 67:185-193.
Maudsley AA, Andronesi OC, Barker PB, et al. Advanced magnetic resonance spectroscopic neuroimaging: experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed 2020: e4309.
Posse S, Otazo R, Dager SR, Alger J. MR spectroscopic imaging: principles and recent advances. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013; 37:1301-1325.
Skoch A, Jiru F, Bunke J. Spectroscopic imaging: basic principles. Eur J Radiol 2008; 67:230-239.
Zhu H, Barker PB. MR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging of the brain. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 711:203-226.
Related Questions
How do you choose between a single and multi-voxel technique?
Can you explain how PRESS works and why is it the most popular MRS method?
How do you choose between a single and multi-voxel technique?
Can you explain how PRESS works and why is it the most popular MRS method?