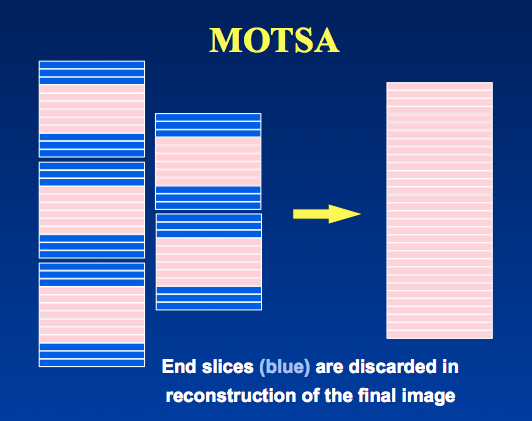
Some variation in signal still occurs at the end slices, so MOTSA extracts only the central portions for each of the overlapping acquisitions to make up the final data set for processing into the MRA projections. The end slices are typically discarded, but may be averaged with those in the adjacent MOTSA section.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Although most vendors refer to this technique as MOTSA, Philips calls their sequence MultiChunk 3D Inflow MRA. In the Philips lexicon, the term "chunk" is equivalent to "slab". Philips also offers a special algorithm to merge chunk borders and reduce/eliminate venetian blind artifacts called CHARM ("CHunk Acquisition and Reconstruction Method").
Other strategies for normalizing signal intensities at the edge slices and correcting for venetian blind artifacts have been proposed. As an alternative to discarding all the overlapping slices, one or two of the overlapping slices may be retained and averaged with the corresponding slices from the next slab acquisition. Other methods such as SLINKY ("SLiding Interleaved Ky) have been proposed that modify reconstruction process but are beyond the scope of this web site.
Blatter DD, Parker DL, Robison RO. Cerebral MR angiography with multiple overlapping thin slab acquisition. Part I. Quantitative analysis of vessel visibility. Radiology 1991; 179:805-811.
What are the major TOF MR artifacts should we know about?