Triple IR is a double IR sequence that includes an additional third slice-selective 180°-inversion pulse shortly before image acquisition module begins. The first two inverting pulses create the dark blood image as described in a prior Q&A. The third inverting pulse nulls the signal from fat. A triple IR sequence can thus be thought of as a double IR sequence plus STIR.
Triple IR sequences thus have two inversion times, denoted as TIa and TIb, and defined in the diagram above. The first inversion time (TIa) is responsible for nulling the signal from blood, while the second (TIb) allows for nulling the signal from fat.
At 1.5 T, the T1 values of blood and fat are approximately 1200 and 230 msec, respectively. Accordingly, the second inversion time for fat (TIb) is shorter than the inversion time for blood (TIa).
As with straightforward STIR imaging, the inversion time to null fat is approximately 160 msec.
Setting TIa is trickier because the effect of the third inversion pulse must be taken into account. This third pulse reinverts the magnetization of inflowing blood, which then must regrow to reach zero again at the time of image acquisition. This means that TIa must be chosen to a longer value than it would be in a double IR sequence. At 1.5T, for example, a value of TIa to null blood would be 1200 msec for triple IR, but only 650 msec for double IR.
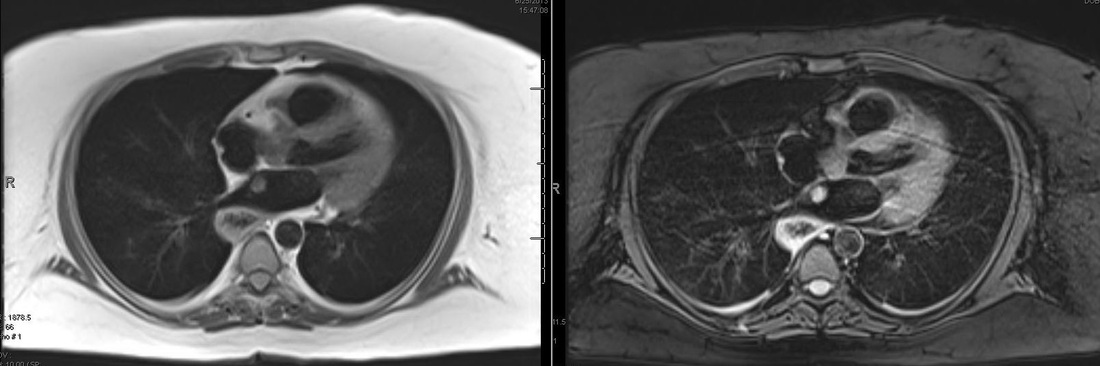
Examples of double and triple IR images at 1.5T are shown below for comparison. Can you find the left atrial myxoma?
As with straightforward STIR imaging, the inversion time to null fat is approximately 160 msec.
Setting TIa is trickier because the effect of the third inversion pulse must be taken into account. This third pulse reinverts the magnetization of inflowing blood, which then must regrow to reach zero again at the time of image acquisition. This means that TIa must be chosen to a longer value than it would be in a double IR sequence. At 1.5T, for example, a value of TIa to null blood would be 1200 msec for triple IR, but only 650 msec for double IR.
Examples of double and triple IR images at 1.5T are shown below for comparison. Can you find the left atrial myxoma?
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Image contrast in the triple IR sequence is largely insensitive to TE, being determined predominantly by choice of inversion times (TI's).
References
Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, et al. "Black blood" T2-weighted inversion recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology 1996; 199:49-57. (Original description of the triple IR technique)
Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, et al. "Black blood" T2-weighted inversion recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology 1996; 199:49-57. (Original description of the triple IR technique)
Related Questions
Why go to the trouble of using a double IR method to suppress blood? Couldn't blood be suppressed with a single carefully selected TI value?
What is STIR?
Why go to the trouble of using a double IR method to suppress blood? Couldn't blood be suppressed with a single carefully selected TI value?
What is STIR?