|
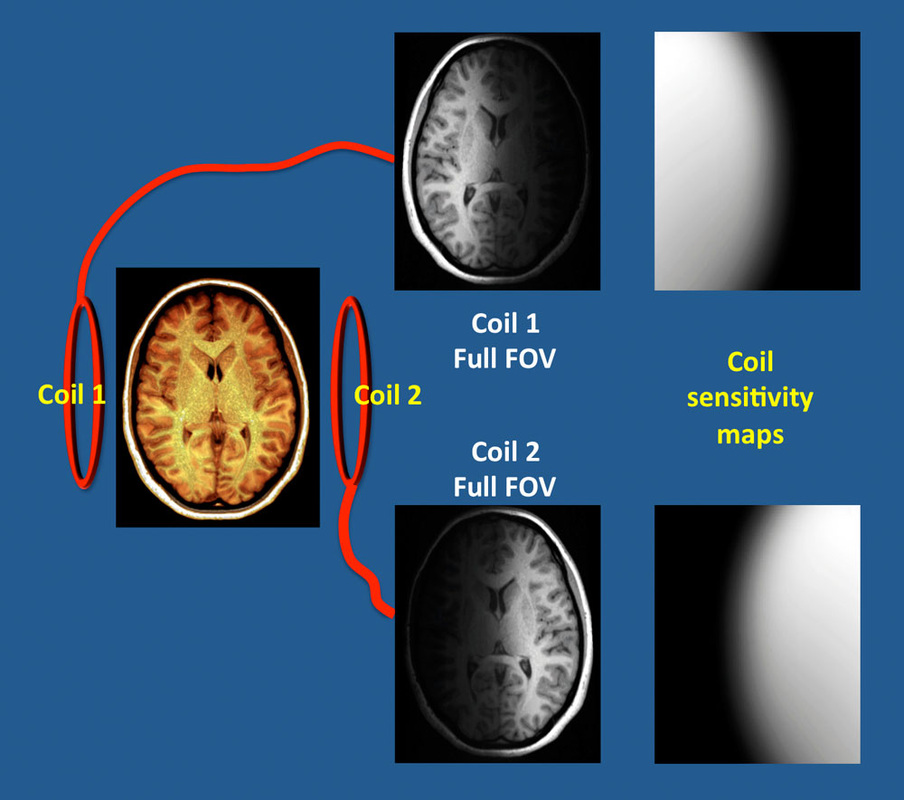
Calculating coil sensitivities are the initial and most important step in the SENSE process. Low-resolution images are acquired separately from each surface coil at full field-of-view. These surface coil images are normalized by dividing them by a low-resolution body coil image. Filtering, thresholding, and point estimation are then applied to the data to generate coil sensitivity maps (shown right). These maps quantify the relative weighting of signals from different points of origin within the reception area of each coil.
|
P2 = A•S2A + B•S2B
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
As you might expect, the reconstruction process is a little more complicated in real life than the above discussion suggests. The typical description for SENSE uses a matrix formulation that includes the following components: I = final image at full FOV; P = partial FOV images with aliasing; S = coarse sensitivity profiles from the individual coils, normalized for uniform signal by the body coil; λ= coarse resolution image from the integrated body coil used to constrain solution during the regularization process; and ψ = noise covariance matrix, representing noise increase due to patient-specific interactions between coil elements.
The inversion process requires solving the following matrix equation using a least squares optimization in the image domain:
I = (SHψ-1S + λ-1)-1SHψ-1P
Blaimer M, Breuer F, Mueller M, Heidemann RM, Griswold MA, Jakob PM. SMASH, SENSE, PILS, GRAPPA. How to choose the optimal method. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2004;15:223-236 [review].
Deshmane A, Gulani V, Griswold MA, Seiberlich N. Parallel MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;36:55-72. (review)
Glockner JF, Hu HH, Stanley DW, et al. Parallel MR imaging: a user's guide. Radiographics 2005;25:1279-1297.
Larkman DJ, Nunes RG. Parallel magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Med Biol 2007;52:R15-R55 [review]
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: Sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 1999; 42:952-962.
Is PI a special type of pulse sequence? Can it be performed with any coil in any direction?
What is parallel imaging? How does this differ from "regular" imaging?