|
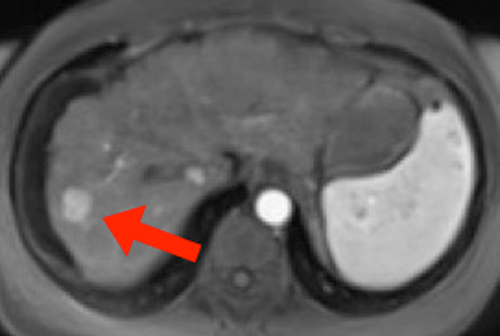
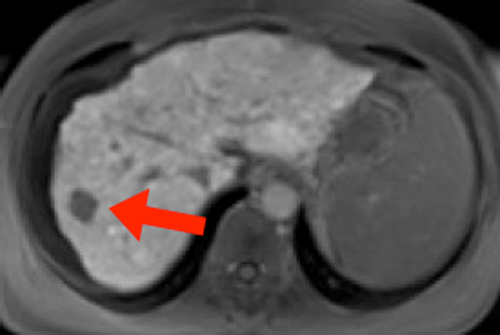
Eovist® (sold as Primovist® outside the USA) is a relatively new gadolinium-based MR contrast agent manufactured by Bayer HealthCare designed for liver imaging. The chemical structure of the molecule closely resembles Gd-DTPA, but with one arm of the ligand attached to the highly lipophylic ethoxybenzyl (EOB) group accounting for liver uptake. The abbreviated generic chemical name for the agent is gadoxetic acid.
|
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Eovist® interferes with complexation methods for serum iron determination and may result in spurious values for 24 hours after injection.
To my knowledge no cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis have been reported with this agent, but it is relatively new to the market. In theory it does offer some protection against gadolinium accumulation in that it is eliminated by hepatobiliary route in patients with renal failure or insufficiency. About 30% of the injected dose can be removed by a single 3-hour dialysis session.
A dose-related prolongation in the QTc interval has been observed in animals and so there is a potential for arrhythmias in humans, especially those on drugs that prolong this interval (quinidine, procainamide, haloperidol, etc).
Baleato-Gonzalez S, Vilanova JC, Luna A, et al. Current and advanced applications of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI in hepaobiliary disorders. RadioGraphics 2023; 43:1-21.
Bayer Healthcare. Eovist® Prescribing Information. (Accurate as of 4/23 but check manufacturer's web site for updates).
Cruite I, Schroeder M, Merkle EM, et al. Gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI of the liver: Part 2, Protocol optimization and lesion appearance in the cirrhotic liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195:29-41.
Davenport MS, Bashir MR, Pietryga JA, et al. Dose-toxicity relationship of gadoxetate disodium and transient severe respiratory motion artifact. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 203:796-802.
Fujita N, Nishie A, Asayama Y, et al. Hyperintense liver masses at hepatobiliary phase gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: imaging appearances and clinical importance. Radiographics 2020; 40:72-94.
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: gadoxetic acid enhanced 3-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging versus multi-detector row computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2009; 33:844-850.
Lee NK, Kim S, Lee JW, Lee SH, et al. Biliary MR Imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA and its clinical applications. Radiographics 2009; 29:1707–1724.
Ringe KI, Husarik DB, Sirlin CB, et al. Gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI of the liver: Part 1, Protocol optimization and lesion appearance in the noncirrhotic liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195:13-28.
Van Beer BE, Pastor CM, Hussain HK. Primovist, Eovist: what to expect? J Hepatol 2012; 57:421-429.
So many gadolinium contrast agents are now available. What are the differences among them?